How Solar Works: From Sunlight to Socket
Dec 9, 2025
3 mins to read
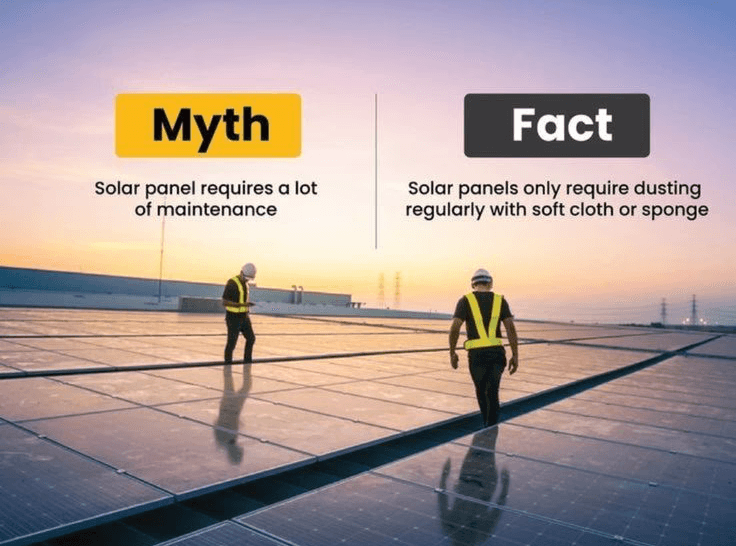
1. Sunlight Hits the Panels
Each solar panel is made up of photovoltaic (PV) cells. When sunlight hits these cells, it knocks electrons loose—this movement creates direct current (DC) electricity.
2. The Inverter Steps In
Homes run on alternating current (AC) electricity, not DC. So the inverter’s job is to convert that DC energy from the panels into usable AC power for your home’s lights, sockets, and appliances.
3. Powering Your Home
Once converted, the electricity flows through your home’s fuse box, powering your devices just like energy from the grid would.
4. Sending Power to the Grid or Battery
If your panels produce more electricity than you’re using, the surplus can either be stored in a battery system for later use, or exported back to the national grid. Under the Smart Export Guarantee (SEG), you can even earn money for the power you send back.
5. Real-Time Monitoring
Most modern solar systems come with apps or displays that let you track performance and energy generation, so you can see your savings in real time.